Sinus rhythm with pvc 240418-Sinus rhythm with pvc ecg strip
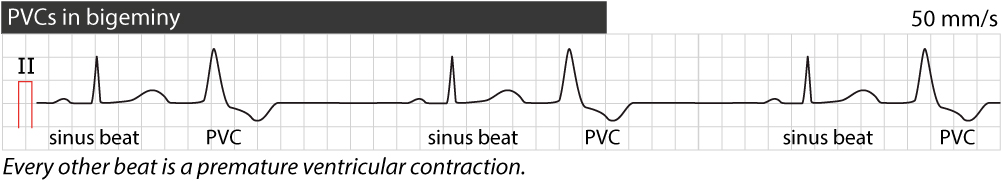
· Sinus rhythm with a triplet and couplet of PVCs Sinus rhythm with a triplet and couplet of PVCs Posted by Unknown at 0300 Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to FacebookShare to Labels Couplet , TripletSinus arrhythmia is a normal physiological phenomenon and it is considered a variation of normal sinus rhythm It is defined as an irregularity in the rate of normal sinus rhythm Its main characteristic on the EKG is a variation in the PP intervals greater than 012 s with a normal P wave morphology 1 2 Minor variation in the PP intervals0221 · If the PVCs continuously alternate with a regular sinus beat, the patient is in bigeminy Likewise, if every third heartbeat is a PVC, then it is named trigeminy PVCs present as heart palpitations in most patients They are usually benign and do not require treatment
1
Sinus rhythm with pvc ecg strip
Sinus rhythm with pvc ecg strip-A premature ventricular contraction, PVC,;, which is an abnormalA premature ventricular contraction (PVC) is a tooearly heartbeat that originates in the ventricles and disrupts the heart's normal rhythm The pattern is a normal beat, an extra beat (the PVC), a slight pause, then a strongerthannormal beat The heart fills with more blood during the pause following the PVC, giving the next beat extra force




Are Your Palpitations Due To Benign Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvcs The Skeptical Cardiologist
· PVCs are probably the second most common rhythm problem I see Atrial arrhythmia, including AF and atrial flutter are the most common This image shows PVCs (beats 2, 4, 6 etc) occurring in what we call a bigeminal pattern Atrial or ventricular beats that appear in an every other beat pattern are referred to as bigeminy0321 · Trigeminy PVC occurring every third beat (two sinus beats followed by a PVC) Quadrigeminy PVC occurring every fourth beat (PVC following three normal beats) Couplet Two consecutive PVCsHere the PVC morphology shows a left bundle branch block pattern (in lead V1) with inferior frontal plane axis (positive QRS in leads 2, 3, aVF)
Rhythm analysis indicates normal sinus rhythm (NSR) at 68 bpm Premature atrial complexes (PACs), Premature junctional complexes (PJCs), and Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are present This encounter shows a normal sinus rhythm with a large amount of ectopySinus Rhythm EKG (ECG) Tracing EKG tracings are printed on grid paper or displayed on a patient monitor These tracings, the EKG waveform, have key features which indicate sinus rhythm or abnormalities (arrhythmias) There are six wave components which are commonly analyzed in determining if the EKG is a sinus rhythmThese wave components provide clues regarding theV Tach may occur in paroxysms of three or more PVC's separated by the underlying rhythm (nonsustained V Tach or Paroxysmal Ventricular Tachycardia), or persist for a long period of time (sustained ventricular tachycardia) The rhythm is usually regular, but it may be slightly irregular
The ECG criteria to diagnose premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) is discussed with 12lead ECG examples including ventricular bigeminy and ventricular trigeminy Treatment is discussed0100 · When is a PVC not a PVC? · I always thought if the rhythm is not regular (which it would not be with PVC's) then to calculate the rhythm on a 6 second strip you count the beats (including ectopic beats) and multiply it by 10 At least thats how I learned it So I think you could say it is sinus rhythm (just not Normal sinus rhythm) with occational PVC's




Ventricular Tachycardia 19 Journal Of Arrhythmia Wiley Online Library




Alivecor Kardia Has A Premature Beat Problem How Pvcs And Pacs Confuse The Mobile Ecg Device The Skeptical Cardiologist
A sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm in which depolarisation of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node It is characterised by the presence of correctly oriented P waves on the electrocardiogram (ECG) Sinus rhythm is necessary, but not sufficient, for normal electrical activity within the heart The term normal sinus rhythm (NSR) is sometimes used to denote a specific type of sinusRhythm analysis indicates sinus tachycardia at over 100 bpm First degree heart block is also present This encounter shows a fast rate over 100 bpm, with a regular rhythm and P waves, indicating sinus tachycardia The extremely long delay between the P wave and QRS indicates first degree heart block2617 · See below Sinus tachy with artifact is a normal but fast rhythm;




Interpreting Ecgs Lead 2



Premature Ventricular Contractions Premature Ventricular Complex Premature Ventricular Beats Ecg Echo
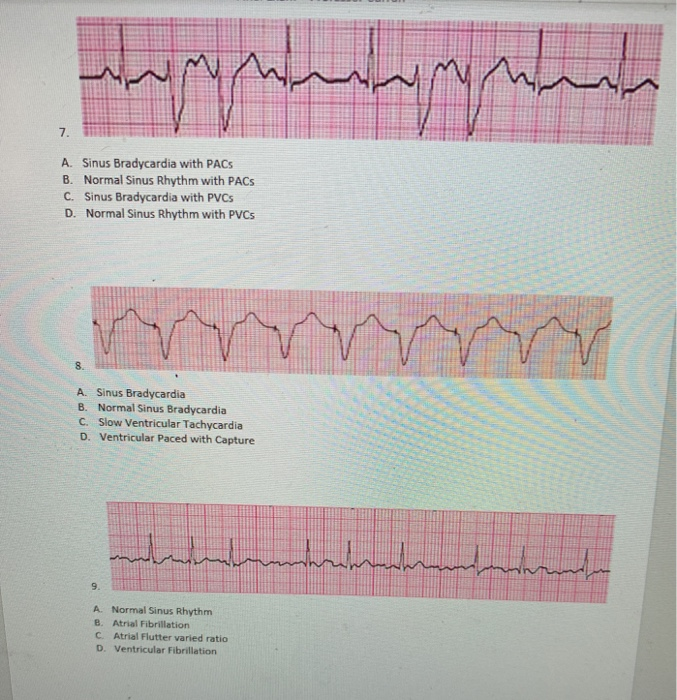
But more commonly as NSVT;Images These are the images used in this course Click on any of the thumbnails to enlarge the image EKG Holter Monitor Schematic diagram of normal sinus rhythm for a human heart as seen on ECG Figure 11 Electrical cells and mechanical cells Figure 121401 · It would be measurable depending on the underlying rhythm In step 5 we need to look at the QRS complex, so during the PVC it is 4 boxes or 016 seconds, it is about 2 boxes on the others or 008 seconds It is normal for the most part but during the PVC it is wider So in step 6 we identify the rhythm and we have sinus bradycardia with PVCs




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvc Boss Rn
· PVCs can occur in isolation or in repeated patterns Two consecutive PVCs are termed doublets while three consecutive PVCs are named triplets It is important to note that three or more consecutive PVCs are classified as ventricular tachycardia If the PVCs continuously alternate with a regular sinus beat, the patient is in bigeminyKardia Advanced Determination "Sinus Rhythm with Wide QRS" indicates sinus rhythm with a QRS, or portion of your ECG, that is longer than expected This could indicate a bundle branch block in which there is a delay in the passage of heart's electrical signals along the bottom of the heartYour heart's normal, or sinus, rhythm is controlled by a natural pacemaker, the sinus node, which creates electrical impulses that travel across the atria to the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood out to your lungs and body in what is known as normal sinus rhythm PVCs occur when ventricle contractions beat sooner than the next expected regular heartbeat, often




Alivecor S Ai V2 Upgraded Ai Powered Algorithm Will Identify Pvcs And Pacs Thereby Reducing Unclassified Mobile Ecgs The Skeptical Cardiologist




Are Your Palpitations Due To Benign Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvcs The Skeptical Cardiologist
· i have a sinus rhythm pvc with rbbb rate 58, shoulder blade pain and left breast pain, and shortness of breath Reply Karen says April 6, 18 at 514 pm I had a holter monitor test done for 24 hrs and it states Rhythm was sinus with episodes of sinus arrhythmia and sinus · PACs momentarily interrupt the normal sinus rhythm by inserting an extra heartbeat Because a PAC can reset the sinus node, there is usually a short pause before the next normal heartbeat occurs As such, PACs are often perceived as a skip in the heartbeat · Sinus Rhythm Changing to Either VT or Wide Complex Atrial Fibrillation Changing to Accelerated Idiove Dropped PACs leading to Junctional Escape Beats Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Showing a Drop Basic EKG Rhythm Test 44 Complete Heart Block Sinus Rhythm with Bigeminal PVCs Atrial fibrillation with a run of monomorphic VT



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Ekg Interpretation
PVCs in patients without structural heart disease, here typically two syndromes are to be considered (ref 3) (1) (most frequent) idiopathic right ventricular outflow tract PVCs/nsVT; · My cardiologist just told me I may have PAC My heart rate went from 125 when it woke me up to 216, called 911, they did an ecg and said it was sinus tacchayardia My rhythm went down to 1 and stayed there until Sunday when I went to the DR, registered me at 150 Upon sitting it went down to 1, after fluids and beta blockers went to 95A premature ventricular contraction (PVC) is a relatively common event where the heartbeat is initiated by Purkinje fibers in the ventricles rather than by the sinoatrial node PVCs may cause no symptoms or may be perceived as a "skipped beat" or felt as palpitations in the chest Single beat PVCs do not usually pose a danger



Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm Aivr Litfl Ecg Library



مممممممممممم A Sinus Bradycardia With Pacs B Chegg Com
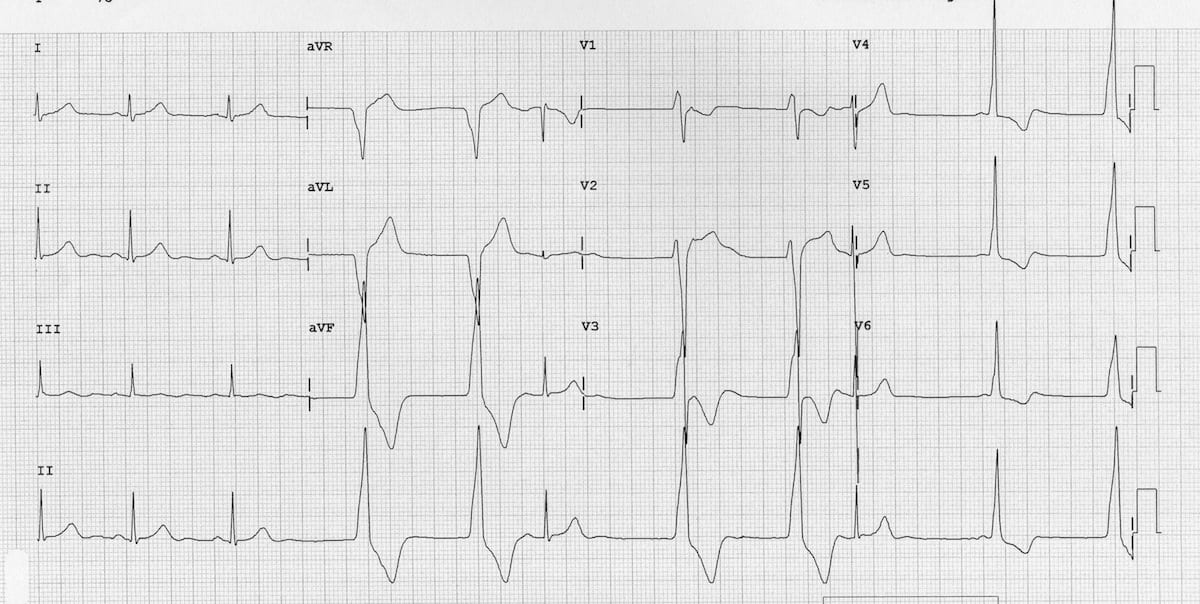
0118 · Sinus rhythm refers to the pace of your heart beat that's set by the sinus node, your body's natural pacemaker A normal sinus rhythm means your heart rate is within a normal range · Sinus Rhythm With Left Bundle Branch Block, PVCs, and Fusion Beats This is a great ECG for teaching your students about some of the different causes of wide QRS This year old man has a sinus rhythm that is around 100 bpm, and his QRS is widened at 148 ms (148 sec)Sinus Arrhythmia ECG (Example 3) Sinus Bradycardia ECG (Example 1) Sinus Bradycardia ECG (Example 2) Sinus Bradycardia ECG (Example 3) Sinus Bradycardia ECG (Example 4) Sinus Tachycardia ECG



Premature Ventricular Contraction Wikipedia




R From T As A Common Mechanism Of Arrhythmia Initiation In Long Qt Syndromes Circulation Arrhythmia And Electrophysiology
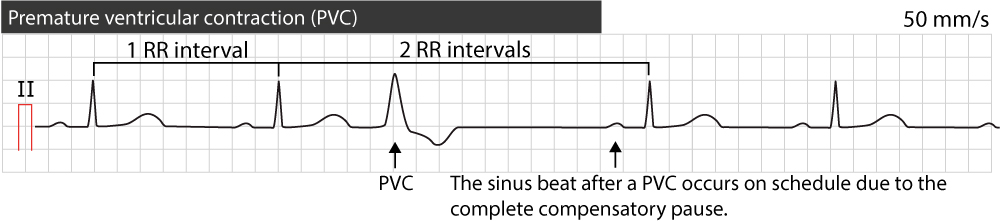
2907 · He had a normal sinus rhythm on ECG, but showed poor R wave progression precordial leads His WBC's were 7800 Creatine Kinase was 95 Echocardiography showed normal LV wall motion His chest xray showed a leftsided spontaneous pneumothorax The left lung was aspirated and expandedThe next sinus beat will occur one sinus cycle after resetting the sinoatrial node The pause will be less than compensatory and the retrograde Pwave is often visible on the STTsegment Ventricular echo This is a rare phenomenon in which the impulse from the PVC is conducted through the atrioventricular node and there it circulates back to the ventricles which areIf your heart feels out of rhythm or "flutters," especially when you have a lot of anxiety, it could be caused by premature ventricular contractions, or PVCs They're the most common reason for



A Junctional Rhythm B Paced With Capture C Third Chegg Com




Premature Ventricular Contraction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Definitions vary regarding 3 or more PVCs;Premature beats that start in your heart's upper chambers are premature atrial contractions, or PACs Those that start in the lower chambers are premature ventricular contractions, or PVCs Watch an animation of a normal heartbeat Testing and treatment Infrequently, premature contractions can be caused by disease or injury to the heartSome authors define three PVCs as a triplet of PVCs;




Ecg Learning Center Test



Premature Ventricular Contraction Article
A consensus definition would be 330 consecutive PVCs with a rate >100bpm described as nonsustained VT (ventricular rhythm if rateAll of my EKG's have been normal except for one that showed sinus arrhythmia and one that had a PAC I have had 3 echos, three 24 hour monitors, and a stress test The most recent testing was in May My heart seems to be getting worse and worse since then with PAC's and PVC's and now this sinus arrhythmiaSinus Rhythm means you heart is beating at a steady consistent rate A first degree AV block means that the electrical signal that starts in the Atria (upper chambers) of the heart and is relayed to the Ventricles (lower chambers) of the heart, is taking too long to get there It's sometimes referred to on the EKG as a prolonged PR time



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Premature Ventricular Contraction Wikipedia
1418 · If the heart rate was normal or greater than 100 it would be called normal sinus rhythm with PVC or sinus tachycardia with PVCs Because PVCs occur from irritable cells in the ventricles, it is very common to see PVC in all rhythms including Aflutter, A fib, and heart blocks So let's talk about managing PVCs>100,with externally caused variations in the appearance of the tracing caused by body movement, poor electrode contact or external electrical interference Sin tachycardia with PVC is normal but fast rhythm,>100, &Whilst others describe this as a 'short burst of VT';




Evaluation And Management Of Ventricular Premature Beats Consultant360
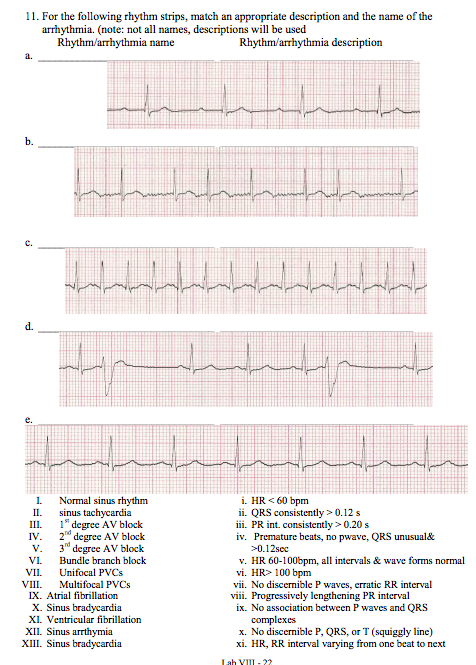



11 For The Following Rhythm Strips Match An Chegg Com
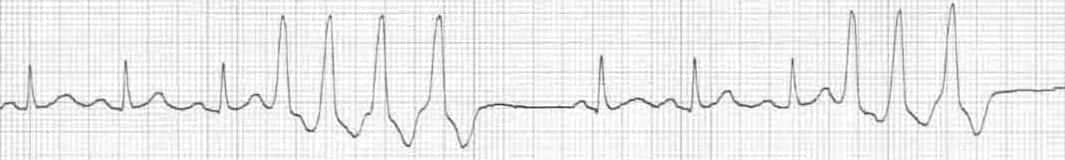
· The sinus node creates electrical impulses that travel across the atria to the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood out to your lungs and body in what is known as normal sinus rhythm In the case of PVCs, the heart doesn't actually skip a beat Instead, an extra beat comes sooner than normal · Nice, clear example of ventricular bigeminy with an underlying sinus rhythm We do not know from this strip if the sinus rhythm is a bradycardia at a rate of about 42 per minute, or if the underlying sinus rhythm is actually at a rate of 85 per minute, with every other sinus beat inhibited by the occurance of a PVCKardia Advanced Determination "Sinus Rhythm with Premature Ventricular Contractions" indicates sinus rhythm with occasional premature ventricular contractions Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are extra heartbeats that originate in the bottom of the heart and usually beat sooner than the next expected regular heartbeat
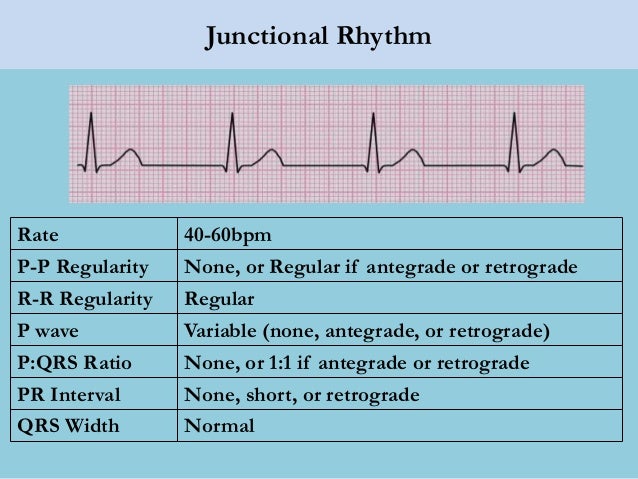



Lec 14 Basic Ecg Interpretation For Mohs




Pin On Nurse Life
· The sinus P waves of the underlying rhythm can be seen just before the PVC in example A and after the PVC in the ST segment in example B These P waves are associated with the underlying rhythm (not the PVC) and usually are hidden within the wide QRS of the premature ventricular contraction0100 · However, if an ectopic focus depolarises early enough — before the arrival of the next sinus impulse — it may "capture" the ventricles, producing a premature contraction Premature contractions ("ectopics") are classified by their origin — atrial (PACs), junctional (PJCs) or ventricular (PVCs)




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Electrocardiogram Demonstrating Underlying Sinus Rhythm With Frequent Download Scientific Diagram




Acls Rhythm Test 2 A 74 Year Old Woman With Chest Pain Blood Pressure 192 90 And Rates Her Pain 9 10 Pdf Free Download




Ecg Learning Center Test



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice




Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvc Treatments Symptoms




Float Nurse Ekg Rhythm Strip Quiz 124




Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvcs Animation Youtube




Pvcs Heart Squad




Ekg Interpretation




Evaluation And Management Of Ventricular Premature Beats Consultant360
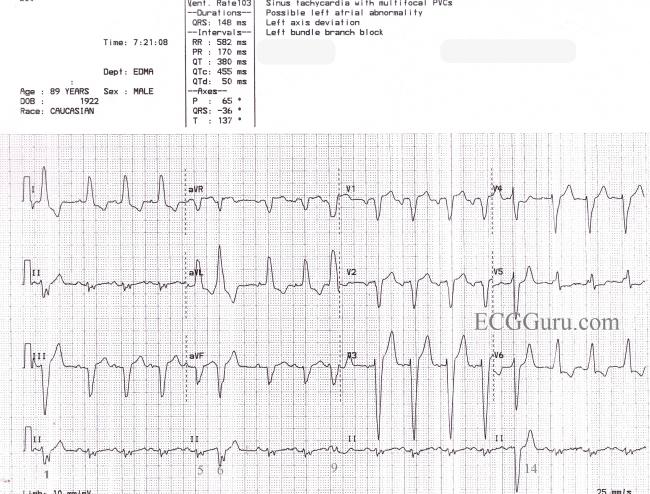



Sinus Rhythm With Left Bundle Branch Block Pvcs And Fusion Beats Ecg Guru Instructor Resources
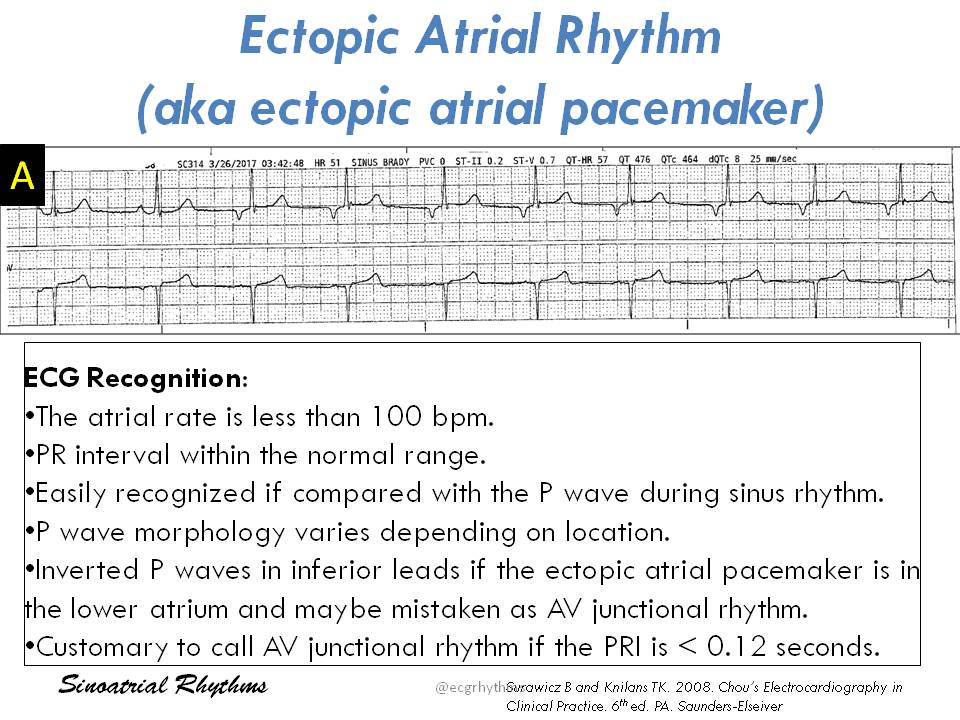



Another Basic Ecg Tweetorial On Sinoatrialrhythms For The Learners Students And Of The Squiggly Lines A Bit Long Feel Free To Add Twitter Thread From Ecgrhythms Arnelc Ecgrhythms Rattibha




Ekg Strips Flashcards Quizlet



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Cardiac Arrhythmia Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvc When The Heart Skips A Beat Hubpages




Posteroseptal Rvot Pvc Sinus Rhythm Positive Stock Photo Edit Now




Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvcs Ecg Review Criteria And Examples Learntheheart Com



Ekg Rhythm Identification



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice



Premature Ventricular Contractions Premature Ventricular Complex Premature Ventricular Beats Ecg Echo



Ventricular Bigeminy Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




The Six Second Ecg Squarespace Pages 1 6 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




Premature Ventricular Contractions Circulation



1
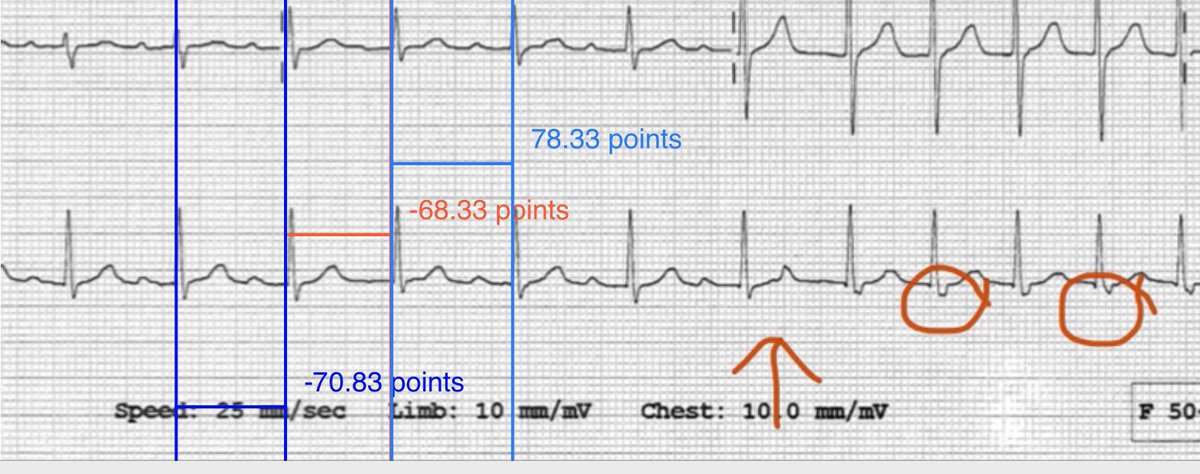



Gareth Wynn Auf Twitter So Ecgs Show Sinus Rhythm And A Narrow Complex Tach In Which Very Unusually Both Onset And Offset Are Captured A Pac Seems To Happen Early Blue Line




Electrophysiology Of The Heart Ecg Monitoring The Ecg




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography



Carolinas Ekg Blog Cmc Compendium
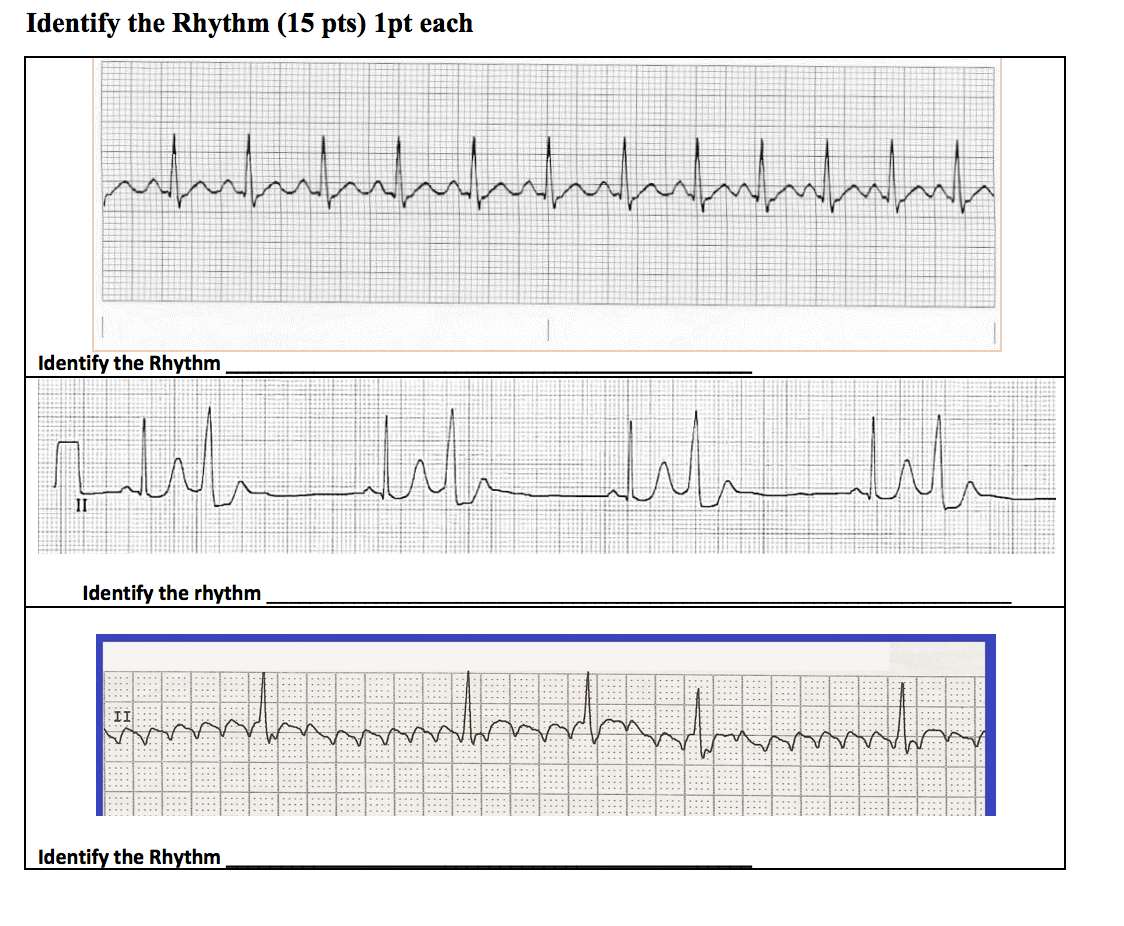



Only Use The Options Provided Answers May Be Used Chegg Com




Bigeminy Wikipedia




Ekg Medic Rhythms Atrial And Vent Flashcards Quizlet




Ventricular Premature Beats Vpb Cardiovascular Disorders Msd Manual Professional Edition
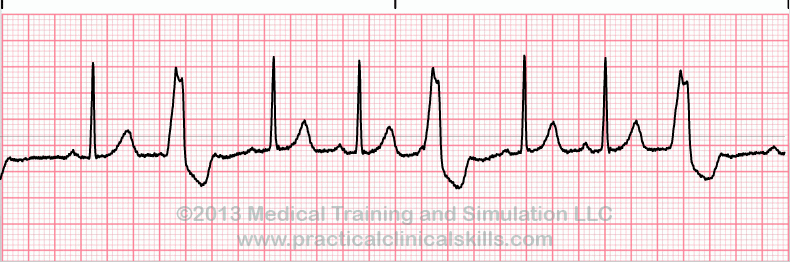



Matters Of The Heart Pvcs Patmac Rn




Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvc Boss Rn
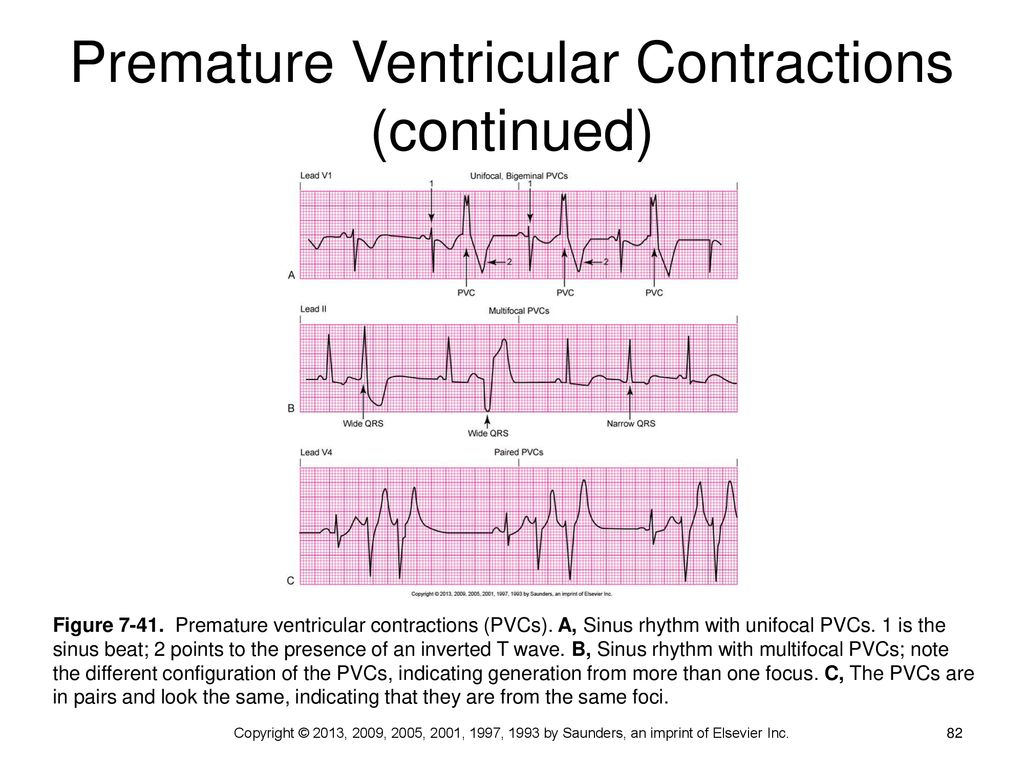



Dysrhythmia Interpretation And Management Ppt Download




Sinus Rhythm And Bigeminal Pvc P Waves Which Follow Pvc Are Blocked Download Scientific Diagram
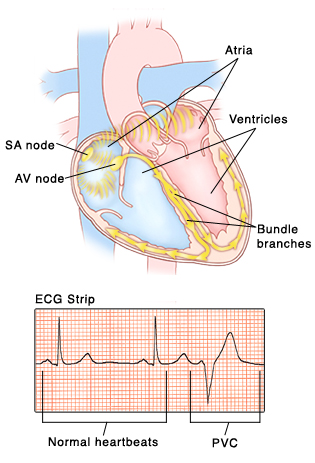



Premature Ventricular Contractions Saint Luke S Health System
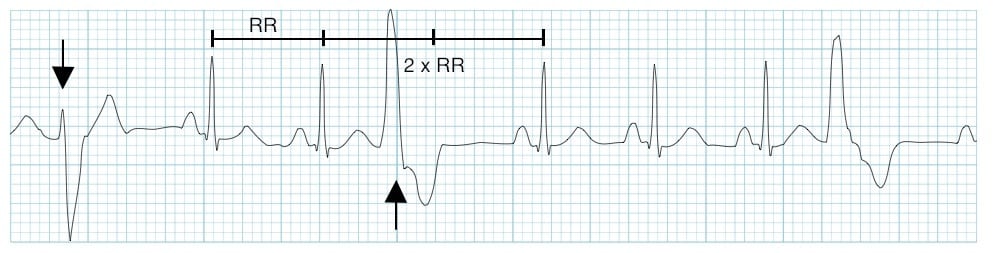



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Sinus Arrhythmia What Is It




Pvc Ecg Example 2 Learntheheart Com




Ekg Medic Rhythms Atrial And Vent Flashcards Quizlet
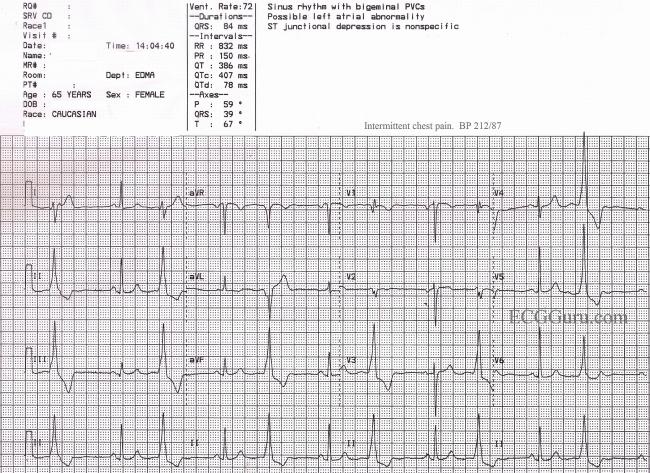



Sinus Rhythm With Ventricular Bigeminy Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Sinus Arrhythmia With Pvc Anteroseptal Infarct Download Scientific Diagram
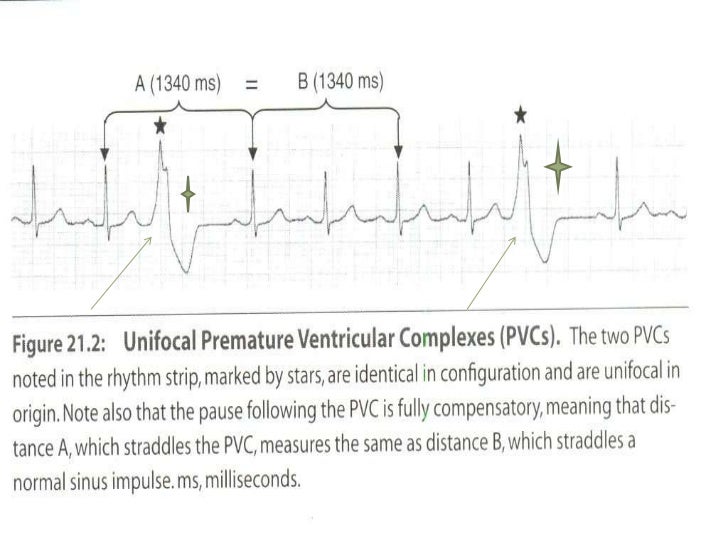



Vpcs




Anterograde And Retrograde Insulated Pathway Conduction Evidenced By Intracardiac Electrogram Morphologies During Premature Ventricular Contractions And Sinus Rhythm Heartrhythm Case Reports
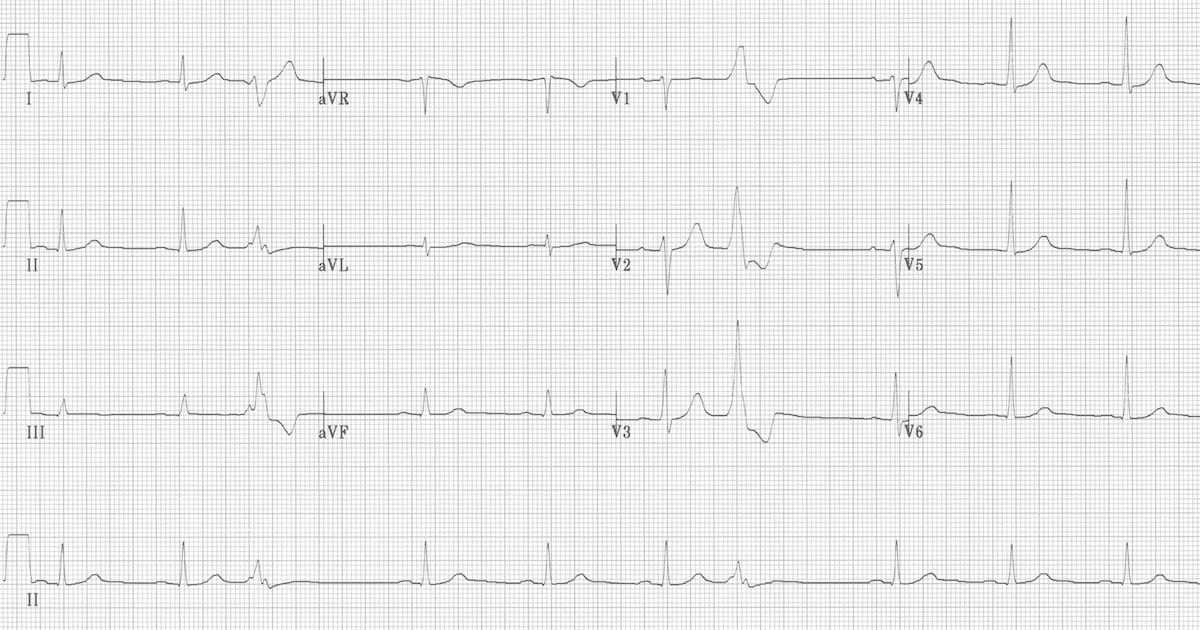



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Pac Pjc Pvc Pdf 5 Minute Speedy Session Telemetry Pac Pjc Pvc Sinus Rhythm Just A Baseline To Compare To The Other Strips Notice That Every P Wave Has Course Hero



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice



Www Bannerhealth Com Media Files Project Bh Careers Practiceekgtest Ashx



Ekg Nov 2 Nov 6



1
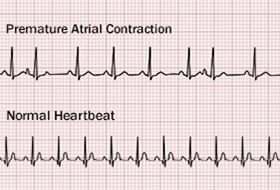



Premature Atrial Contractions Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment




Ecg Educator Blog Ventricular Bigeminy
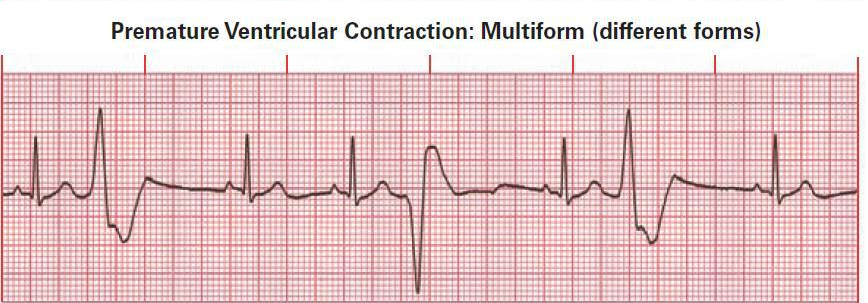



Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvc Boss Rn




Predicting The Risk Of Sudden Cardiac Death Lerma 16 The Journal Of Physiology Wiley Online Library



1




Multiform Premature Ventricular Contractions A Reason Not To Ablate Heart Rhythm
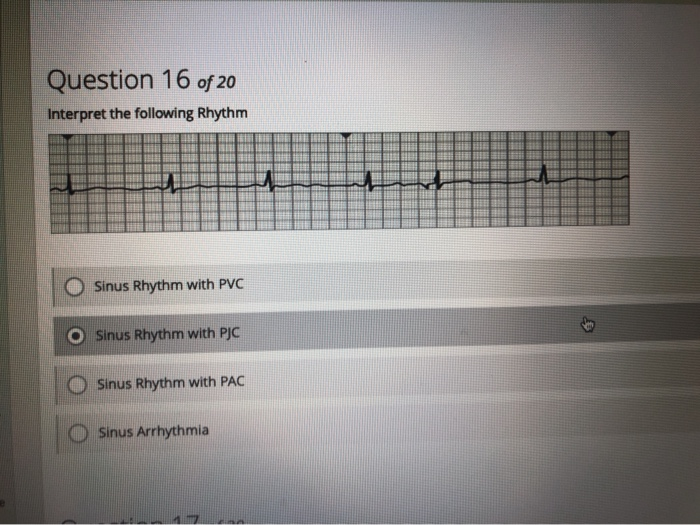



Question 16 Of Interpret The Following Rhythm O Chegg Com




Precordial Leads V1 V2 And V3 Of Sinus Rhythm And A Premature Download Scientific Diagram
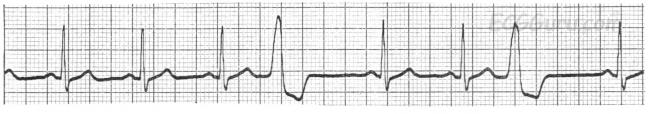



Ecg Basics Normal Sinus Rhythm With Premature Ventricular Contractions Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



A Simulated Monitor Showing The Stock Footage Video 100 Royalty Free Shutterstock



Why Are Premature Ventricular Contractions Common In Healthy Persons Quora




Ventricular Rhythms Ecg Collection Alila Medical Images




Telemetry Technician Course Pvc Practice Strips Class 6




Sage Books Acute Illness Management
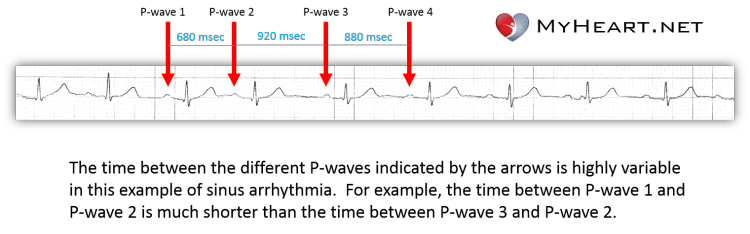



Sinus Arrhythmia What Is It




Premature Ventricular Complexes Medictests




Rcp 122 Ekg 2 Flashcards Quizlet



Q Tbn And9gcqts24zy8 O4ata1y1l95dt16bmfklbcgfih0gkrhxza2ulzs Y Usqp Cau




Premature Ventricular Contraction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




What Is Causing Your Cardiac Flip Flops Pvcs Revisited With Kardia S Advanced Determinations The Skeptical Cardiologist
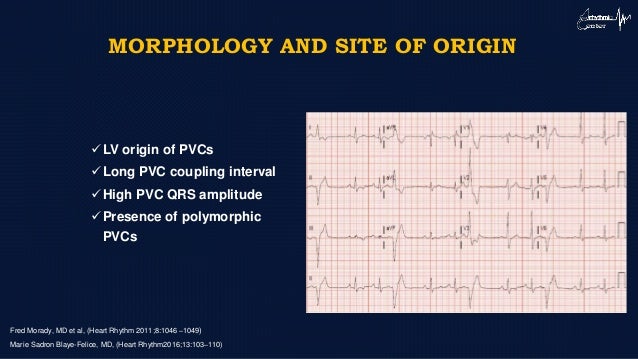



Novel Approaches To Pvc




Cv Physiology Abnormal Rhythms Definitions




Lower Than Expected Burden Of Premature Ventricular Contractions Impairs Myocardial Function Lie 17 Esc Heart Failure Wiley Online Library




Palpitations And Skipped Beats The Gentle Touch That Worries So Many Joel Kahn Md Integrative Cardiologist




Ecg Learning Center Test




Ectopic Complexes And Rhythms Thoracic Key




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Sinus Rhythm And Bigeminal Pvc P Waves Which Follow Pvc Are Blocked Download Scientific Diagram


コメント
コメントを投稿